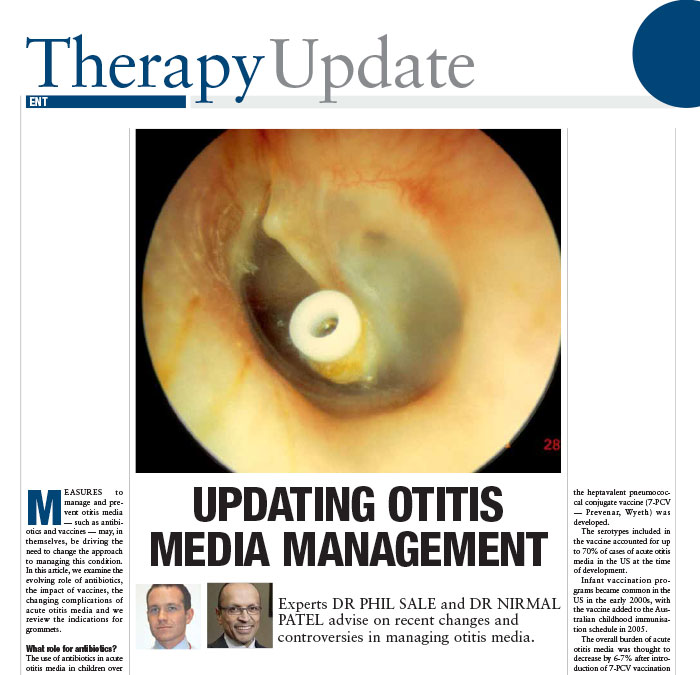
Recurrent ear infections typically present in 1-3 year old children will a painful ear and fevers. The condition is usually due to a combination of poor Eustachian tube function and/or nasal obstruction. Day care and smoking exposure can worsen the scenario.
Treatment is initially with antibiotics if under the age of 2. If the child has recurrent infections where the pus remains in the ears despite antibiotics then surgery may be recommended. This is done to reduce the frequency severity and intensity of infections; furthermore surgery reduces the risk of serious complications of middle ear infections (such brain abscess, hearing loss and facial nerve weakness).
As a child gets older often the painful ear infections will reduce and painless fluid develops in the middle ear which can cause conductive hearing loss. This is a correctable situation. Nasal sprays and decompression methods to open the Eustachian tube are often used first. If this fails and hearing loss is present in both ears for more than 3 months or one ear for more than 6 months the surgery is recommended.
Surgery involves grommet (or middle ear ventilation tube). This is a day surgery procedure performed under general anaesthesia, with a 4-6 hour stay in hospital. The child usually requires very little post-operative pain management, as there is a decompression of the middle ear pressure and a near immediate relief felt by the child.
More information is available on the Sydney Hills ENT Clinic website.
OTHER DISEASE PROCESSES
Shared decision grid for parents and caregivers regarding surgical options of Otitis Media with Effusion
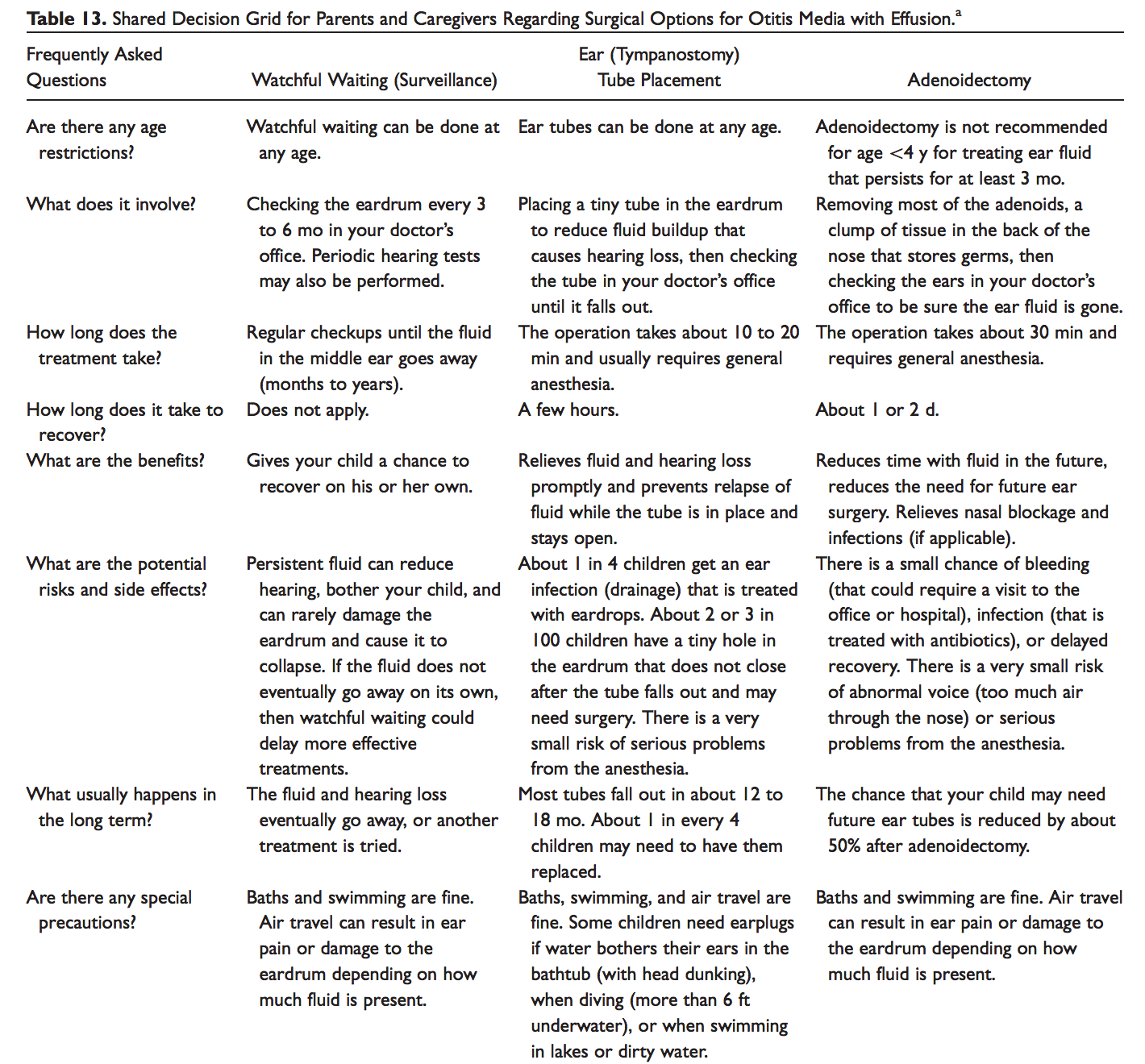
Credit: Clinical Practice guidelines Feb 2016 Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery.
OTHER DISEASE PROCESSES
Got a question you would like to ask Dr Nirmal Patel?